Is it time for a magnesium top-up?

You get muscle cramps
If you aren't getting enough magnesium in your diet, you might experience muscle cramps and twitches.2 This is because magnesium is responsible for the contraction and relaxation of our muscles. It does this by helping to balance calcium levels in our muscle cells.2
You're tired
Are you lacking in energy? One of the most important roles that magnesium plays in the body is the production of energy. It is used in our cells in the formation of a molecule that provides energy for the majority of metabolic processes in the body, called adenosine triphosphate (ATP).2
You exercise
Magnesium is excreted from the body in water, so if you exercise, chances are you may lose some magnesium through your sweat.3 Increasing your dietary intake of magnesium could help compensate for this loss.3
You get PMS
Women who experience premenstrual syndrome (PMS) have lower levels of magnesium in their plasma than women who don't get PMS.4 If you experience PMS symptoms such as mood changes, irritability or breast tenderness, then taking magnesium might help provide some relief if your dietary intake of this important mineral is inadequate.4
You're over 51 years old
Research from the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) indicates that the diets of many older Australians don't supply the recommended quantities of magnesium.1
Almost half of all Australian men over 51 years old (46.5%) don't consume their estimated average requirement (EAR) of 350mg per day, while 30% all women of the same age consume less than their EAR (265mg per day).1
Because magnesium is important for maintaining healthy bones, consuming enough magnesium is important for older people.2

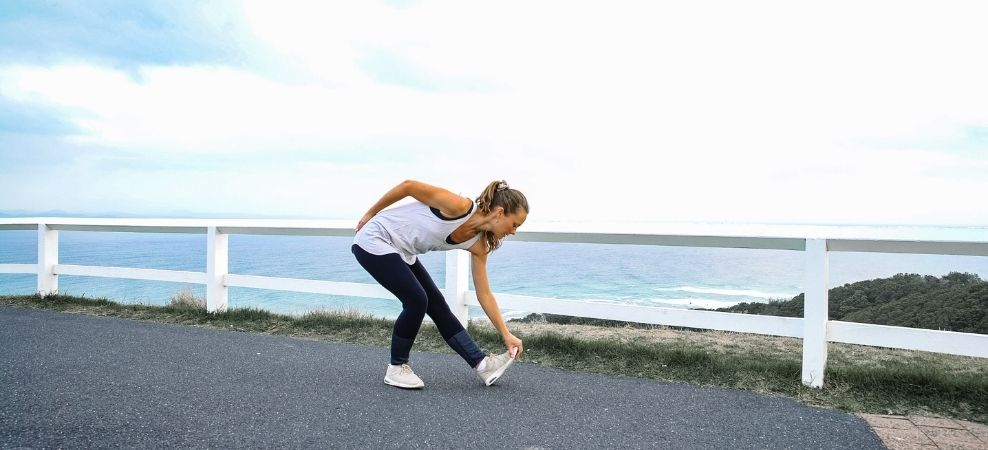
Where can I get more magnesium from?
There are many foods you can include in your diet that are rich in magnesium, including brazil nuts, almonds, cereals (oats, all bran), brown rice, spinach, chickpeas and bananas.2
Choosing a magnesium supplement
When selecting a supplement, choose a product that contains a highly bioavailable, easily absorbed source of magnesium, such as magnesium glycinate as found in Fusion Magnesium Advanced.
If swallowing large tablets is difficult for you, consider taking a powdered supplement that can be dissolved in water, smoothies or juice - these have the added benefit of being suitable to use in your drink bottle when you're training - try delicious Fusion Magnesium Advanced Lemon-Lime Zing Powder.
Always read the label and follow the directions for use.
References
- Australian Bureau of Statistics, Food Standards Australia New Zealand. Australian health survey: usual nutrient intakes 2011-12. Commonwealth of Australia, 2015.
- Volpe SL. Oregon State University 2019. Viewed 19 Sep 2019,lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/minerals/magnesium
- Nielsen FH. Magnes Res2006;19(3):180-189.
- Moslehi M, et al. Biol Trace Elem Res 2019 doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01672-z. [Epub ahead of print].